The technology first gained attention in the 1950s for use in submarines and has since developed into a mainstream tool in modern automation and safety systems. Ultrasonic sensing exists today because many environments require reliable, non-contact detection methods that work even when light, color, or dust make optical sensors ineffective.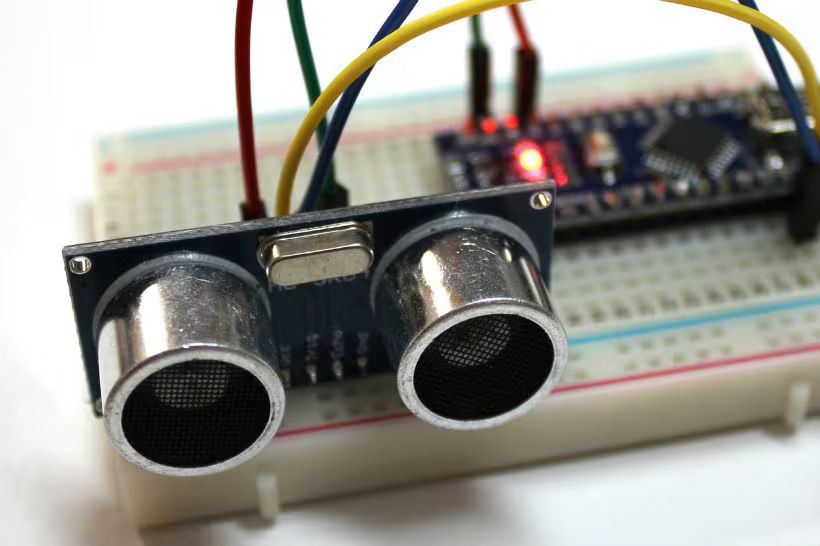
Importance
Ultrasonic sensors matter today because they solve critical challenges in automation, navigation, and safety. Unlike vision systems, these sensors do not rely on visible light and therefore perform well in dark, dusty, or reflective environments.
Key reasons why ultrasonic sensors are important include:
-
Automotive safety: Used in parking assistance and collision avoidance.
-
Industrial automation: Supports precise material handling and level monitoring in tanks.
-
Healthcare: Applied in diagnostic imaging and medical devices.
-
Robotics: Enables obstacle detection and navigation in autonomous machines.
-
Smart cities: Used in traffic management, waste monitoring, and energy systems.
This technology benefits manufacturers, engineers, researchers, and consumers by enabling safer and more efficient systems across multiple industries.
Recent Updates
The ultrasonic sensor market has seen notable changes and growth trends over the past year.
-
2024–2025 Market Growth: According to global market reports, ultrasonic sensor demand has increased due to the rise of autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. Growth projections suggest a CAGR of around 8% through 2030.
-
Automotive Integration: In 2024, many leading car manufacturers began integrating advanced ultrasonic sensors for driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
-
Miniaturization: Research in 2025 shows progress in smaller, energy-efficient ultrasonic sensors suitable for wearables and IoT devices.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Recent pilot projects in Europe (2024) used ultrasonic sensors for smart waste collection and water level monitoring to improve sustainability.
These developments highlight how the technology continues to expand its influence across different industries.
Laws or Policies
The use of ultrasonic sensors is influenced by international and national regulations. Policies often focus on safety standards, product quality, and usage in specific sectors.
-
Automotive Regulations: Countries such as the United States, Japan, and members of the European Union mandate safety features in vehicles, indirectly driving adoption of ultrasonic sensors.
-
Medical Devices: Healthcare applications are regulated by authorities like the FDA (U.S.) and CE marking in Europe, ensuring ultrasonic devices meet strict standards.
-
Industrial Safety: ISO standards provide guidelines for ultrasonic measurement tools to ensure accuracy and workplace safety.
-
Environmental Policies: Government programs promoting smart cities often encourage the use of ultrasonic sensing in water management, traffic systems, and sustainable energy infrastructure.
Compliance with these laws ensures that the technology is safe, reliable, and fit for both industrial and consumer use.
Tools and Resources
Professionals and learners can access a variety of tools and resources to understand and apply ultrasonic sensors.
Common tools and platforms include:
-
Datasheets and application notes from manufacturers like Honeywell, Siemens, and Pepperl+Fuchs.
-
Simulation software such as MATLAB and COMSOL Multiphysics for modeling ultrasonic behavior.
-
Online calculators for measuring distance and pulse response in ultrasonic sensing.
-
Educational platforms like IEEE Xplore and ResearchGate for research papers.
-
Open-source hardware projects on platforms such as Arduino and Raspberry Pi for practical learning.
These resources make it easier for engineers, students, and researchers to experiment, test, and improve their understanding of ultrasonic technology.
Applications Overview Table
| Application Area | Role of Ultrasonic Sensors | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Parking assist, collision warning | Reverse parking sensors, ADAS systems |
| Industrial Automation | Level monitoring, object detection | Conveyor systems, storage tanks |
| Healthcare | Medical diagnostics, patient monitoring | Ultrasound imaging, non-invasive devices |
| Robotics | Navigation and obstacle avoidance | Autonomous delivery robots, drones |
| Smart Infrastructure | Traffic, waste, and water management | Smart bins, flood detection, traffic flow |
FAQs
Q1: What is the working principle of ultrasonic sensors?
Ultrasonic sensors work by emitting high-frequency sound waves and measuring the time it takes for the echo to return after hitting an object. The distance is calculated using the speed of sound.
Q2: How are ultrasonic sensors different from infrared sensors?
Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves, while infrared sensors rely on light. Ultrasonic devices are more effective in dark or dusty environments, while infrared may perform better in applications requiring higher speed detection.
Q3: Are ultrasonic sensors safe for humans and animals?
Yes, ultrasonic sensors operate at frequencies above the human hearing range, making them safe for use in consumer and industrial products.
Q4: What industries benefit most from ultrasonic sensors?
Industries such as automotive, manufacturing, healthcare, robotics, and environmental monitoring use ultrasonic sensors extensively due to their precision and versatility.
Q5: What are the limitations of ultrasonic sensors?
They can face challenges with very soft surfaces that absorb sound waves, extreme temperatures, or strong wind conditions that affect accuracy.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic sensors represent a versatile and reliable technology that bridges multiple fields, from automotive safety to healthcare and environmental management. Their ability to function in complex environments makes them essential in today’s automation-driven world.
The latest advancements show increasing integration with IoT, robotics, and sustainable city projects. Regulatory frameworks ensure safety and standardization, while resources and tools make the technology more accessible to both professionals and learners.
By exploring the fundamentals, applications, and emerging trends of ultrasonic sensors, it becomes clear that this technology will continue to shape innovation across industries.