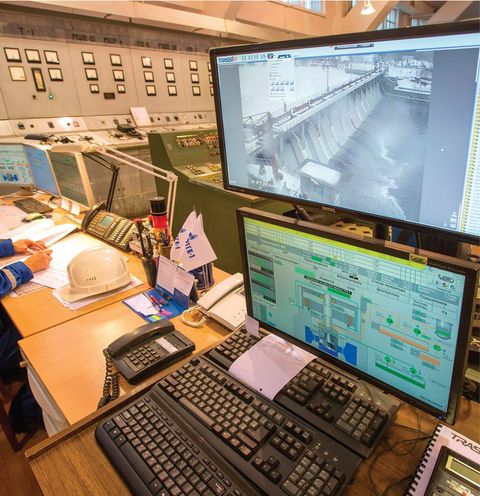
This guide explores the context, importance, latest updates, policies, and practical resources connected to industrial digital twins. Readers will also find frequently asked questions and simple insights to help understand how this technology is shaping modern industries.
Context: What Industrial Digital Twin Is and Why It Exists
A digital twin is designed to mirror physical assets in a way that helps professionals test, optimize, and improve processes without disrupting real-world operations.
-
Definition: A digital twin is a digital model that reflects real-time data, behaviors, and states of a physical system.
-
Purpose: To simulate scenarios, identify problems before they occur, and enable more informed decision-making.
-
Origin:The idea gained attention in the early 2000s, but adoption expanded rapidly with the growth of sensors, IoT (Internet of Things), and advanced analytics.
In manufacturing, for example, a digital twin of a production line helps monitor equipment, predict maintenance needs, and improve efficiency. In energy, digital twins are used to optimize wind farms or power plants.
Importance of Industrial Digital Twin Today
Digital twin technology has become more significant in the last decade because industries demand efficiency, sustainability, and innovation.
Who it affects:
-
Manufacturers: To improve productivity and reduce downtime.
-
Healthcare organizations: To simulate patient outcomes and device performance.
-
Construction and infrastructure firms: To manage large-scale projects and assets.
- Energy sector: To optimize renewable and conventional energy operations.
Problems it solves:
-
Equipment failures by enabling predictive maintenance.
-
Wasted resources by identifying inefficiencies.
-
Safety risks by simulating real-world conditions digitally.
-
High costs of experimentation by providing virtual models instead of physical prototypes.
Digital twins also support sustainability goals by reducing waste and lowering emissions through smarter operations.
Recent Updates and Trends
The last few years have seen rapid advancements in digital twin technology.
2024: Many industries expanded adoption of AI-driven digital twins, combining machine learning with simulation for more accurate predictions.
2023: Automotive companies used digital twins to accelerate electric vehicle (EV) design and testing, cutting down development time.
2022–2024: The global digital twin market showed double-digit growth, with reports highlighting its importance in aerospace, healthcare, and energy.
Ongoing trend: Integration with cloud computing and 5G technology allows real-time monitoring at a larger scale.
These updates show how digital twin technology is no longer experimental but part of strategic business planning worldwide.
Laws, Policies, and Regulations
The growth of digital twins is influenced by data protection laws, safety regulations, and government programs supporting Industry 4.0.
-
Data Privacy: Since digital twins often collect real-time data, compliance with laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. is necessary.
-
Cybersecurity Standards: Organizations must follow guidelines like NIST Cybersecurity Framework in the U.S. to secure industrial digital twins.
-
Government Programs: Many countries, including Germany and Japan, promote Industry 4.0 initiatives that encourage digital twin adoption.
- Environmental Regulations: Using digital twins to optimize energy usage aligns with emission reduction targets and sustainability policies worldwide.
These frameworks shape how industries design and manage digital twin systems responsibly.
Tools and Resources
Digital twin implementation involves platforms, software, and knowledge resources.
Common Platforms:
Siemens Digital Industries Software – widely used for manufacturing simulation.
PTC ThingWorx – focuses on IoT integration and smart factory solutions.
IBM Digital Twin Exchange – provides templates and solutions for multiple industries.
Microsoft Azure Digital Twins – cloud-based modeling and analysis.
Helpful Resources:
Industry reports from Gartner and McKinsey on digital twin adoption.
Educational platforms like Coursera and edX offering courses on IoT and digital twins.
Professional networks such as Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) for standards and collaboration.
Key Features and Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-time monitoring | Immediate insights into equipment and processes |
| Predictive maintenance | Avoids costly breakdowns and improves reliability |
| Simulation and modeling | Tests scenarios without physical risks |
| Data-driven decision-making | Improves accuracy in planning and strategy |
| Integration with IoT and AI | Enables automation and intelligent analytics |
This combination of features explains why industries view digital twins as a critical tool in modernization.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between a digital model and a digital twin?
A digital model represents a design, while a digital twin includes real-time data and ongoing interaction with the physical system.
Q2. Which industries benefit most from digital twins?
Manufacturing, healthcare, energy, construction, and aerospace are among the top sectors adopting digital twin technology.
Q3. Is a digital twin the same as simulation software?
No. Simulation software is static, while digital twins update continuously with real-world data.
Q4. How does AI improve digital twins?
Artificial intelligence enhances predictions, automates analysis, and identifies patterns that humans may overlook.
Q5. Are digital twins secure?
They can be secure when built with strong cybersecurity measures, but risks exist if data protection laws and frameworks are not followed.
Conclusion
Industrial digital twin technology represents a shift in how industries operate, innovate, and maintain systems. It provides a bridge between physical and digital worlds, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved efficiency.
With continuous updates, alignment to regulations, and support from government and industry programs, digital twins are expected to expand across sectors in the coming years. For businesses, researchers, and policymakers, understanding digital twins means being prepared for the next phase of industrial transformation.